Mechanism of Stabilization of Helix Secondary Structure by Constrained Cα-Tetrasubstituted α-Amino Acids
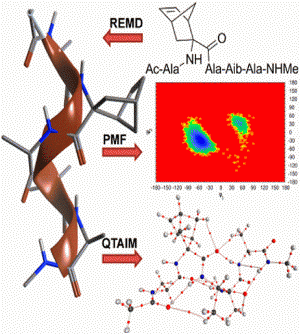
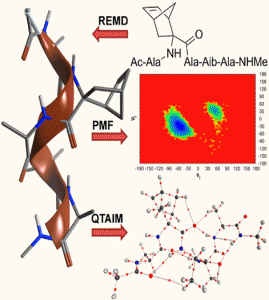
The theoretical basis behind the ability of constrained Cα-tetrasubstituted amino acids (CTAAs) to induce stable helical conformations has been studied through Replica Exchange Molecular Dynamics, Potential of Mean Force and Quantum Theory of Atoms In Molecules calculations on Ac-L-Ala-CTAA-L-Ala-Aib-L-Ala-NHMe peptide models. We found that the origin of helix stabilization by CTAAs can be ascribed to at least two complementary mechanisms limiting the backbone conformational freedom: steric hindrance predominantly in the (+x,+y,-z) sector of a right-handed 3D Cartesian space, where the z axis coincides with the helical axis and the Cα of the CTAA lies on the +y axis (0,+y,0), and the establishment of additional and relatively strong C-H∙∙∙O interactions involving the CTAA.
J. Phys. Chem. B, 2015, 119 (4), 1350–1361
DOI: 10.1021/jp510775e




comments